Toolmaking Solutions
Automotive Toolmaking Solutions for advanced forming technology
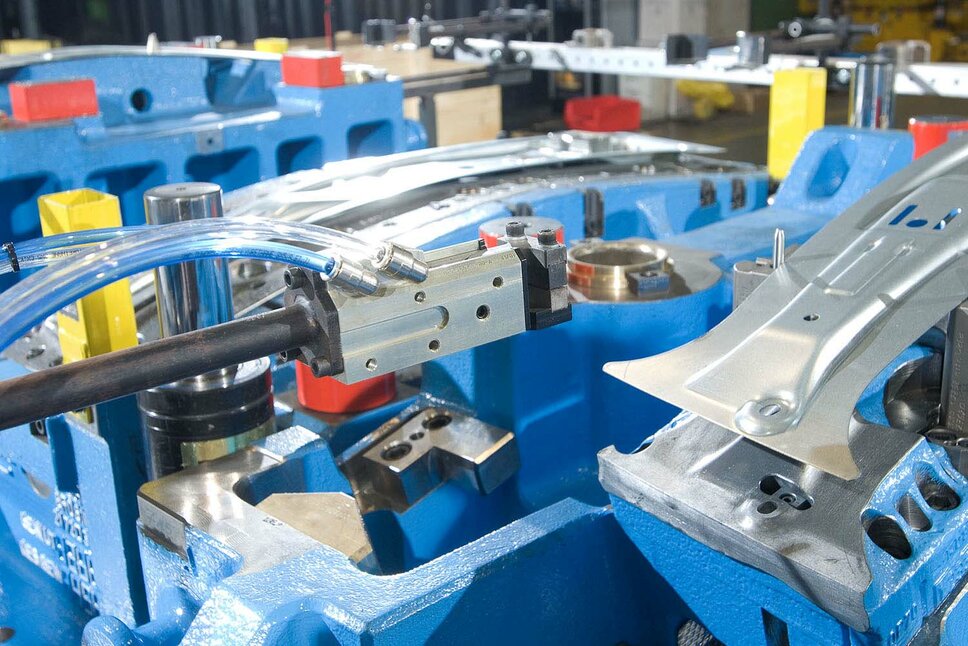
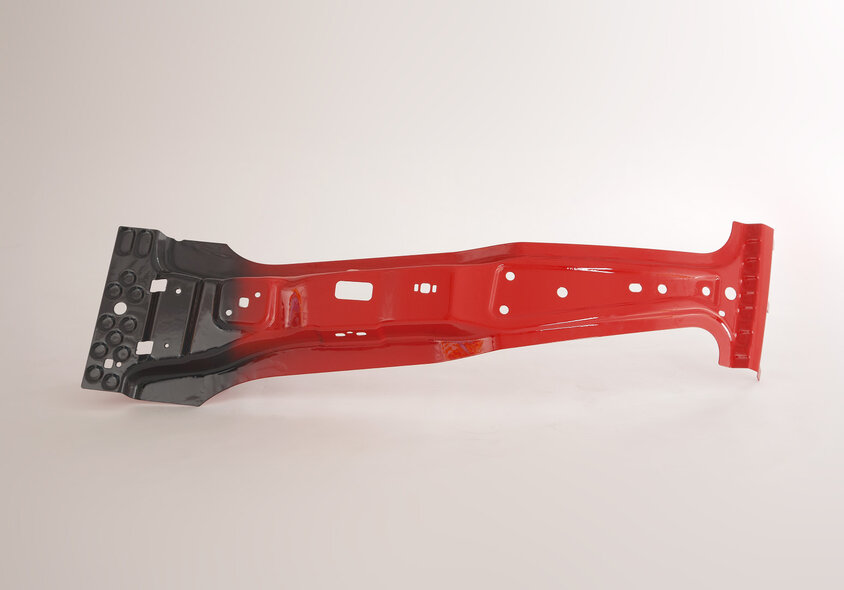
As leading tooling manufacturer for automotive requirements, we distinguish ourselves through our competence in cold and hot forming. We offer our clients customized toolmaking solutions for ultra-high-strength, the forming of aluminum, as well as carbon products, precisely tailored to their individual tooling needs. Our approach focuses on maximizing the lifespan of pressing and stamping tools and enhancing process efficiency through the use of advanced technologies and innovative materials in tool manufacturing. Our extensive tooling expertise encompasses all phases of the forming process – from initial CAD conception and prototype development to series production and joining technology.
TOOLMAKING SOLUTIONS FOR HOT FORMING
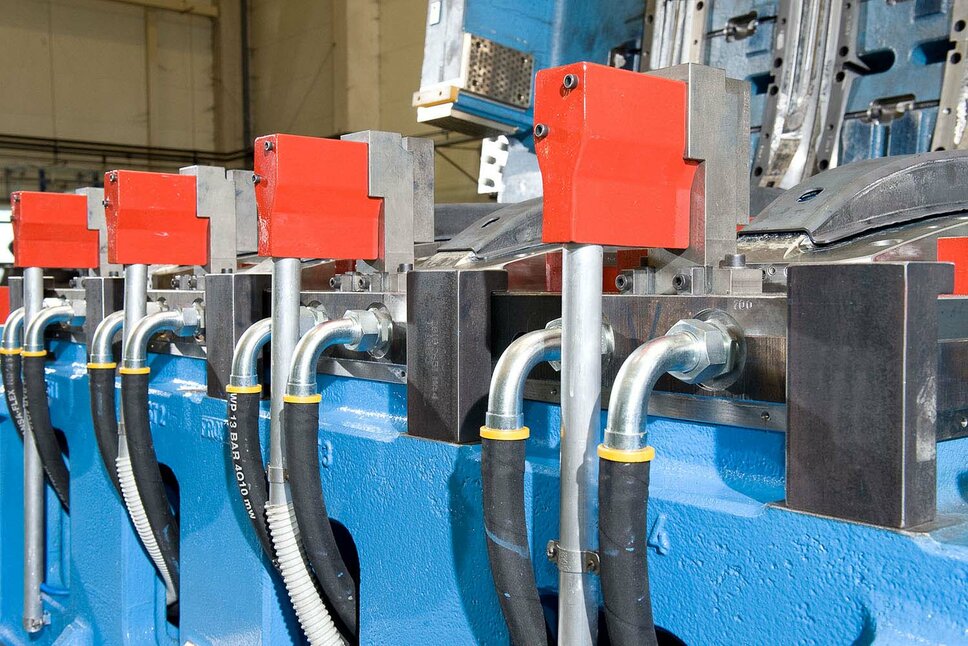
Explore the future of lightweight construction with our advanced toolmaking solutions for hot forming! Optimize your production with our tailor-made solutions in tool manufacturing: from high-quality materials and innovative sensor technology to specialized cooling systems.
TOOLMAKING SOLUTIONS FOR COLD FORMING OF HIGH-STRENGTH STEEL
Increase the efficiency of your metal processing with our innovative toolmaking solutions and high-quality for cold forming! Our transfer and line cold forming tools, equipped with advanced gripper and robot handling, offer the perfect combination of strength and precision to meet even the most demanding requirements in metal forming.
Our toolmaking service portfolio at a glance
Was uns auszeichnet
QUALITY ASSURANCE IN TOOLMAKING
Quality assurance is our top priority in toolmaking. By consistently improving our processes and driving continuous innovation, we ensure that our toolmaking solutions meet the highest standards. We have implemented comprehensive quality management systems that allow us to closely monitor and optimize every step of production. Our tool shop is certified according to the international standard DIN EN ISO 9001:2015, highlighting our commitment to adhering to strict quality standards. This certification is a testament to our ability to deliver consistent, high-quality results in tool manufacturing and provides our customers with the confidence to rely on us as a trusted partner.
Learn more about our certified quality in toolmaking and discover how we successfully implement your projects with the highest standards. Read on and let yourself be convinced by our customized tooling solutions.
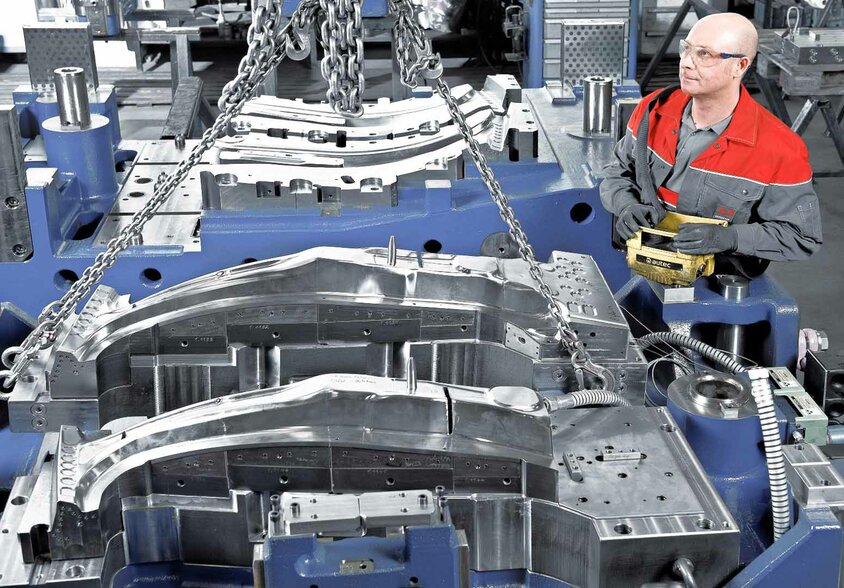
CONTRACT MANUFACTURING
In our tool shop, we offer comprehensive contract manufacturing services, combining top expertise in mechanical machining, laser cutting, metrology, and tool tryout. With state-of-the-art technologies and years of experience in toolmaking, we ensure that every component is manufactured with precision and meets the highest quality standards.
Read on to learn more about how our contract manufacturing and toolmaking solutions can efficiently and successfully support your projects.